What Is a V6 Engine?
A V6 engine is an engine with six cylinders arranged in two rows of three generally laid out in a V-shaped formation. As an innovation on the traditional straight-six design, this layout was designed to make engines more compact without sacrificing performance.
V6 engines became popular choices for manufacturers of everything from sports cars to mid-size sedans to full-size trucks and have some distinct features and advantages
V6 Engine Specs
To dig into the differences between V6 and straight-six engines, we'll look at a few key specs that set the two apart.
Firing Order
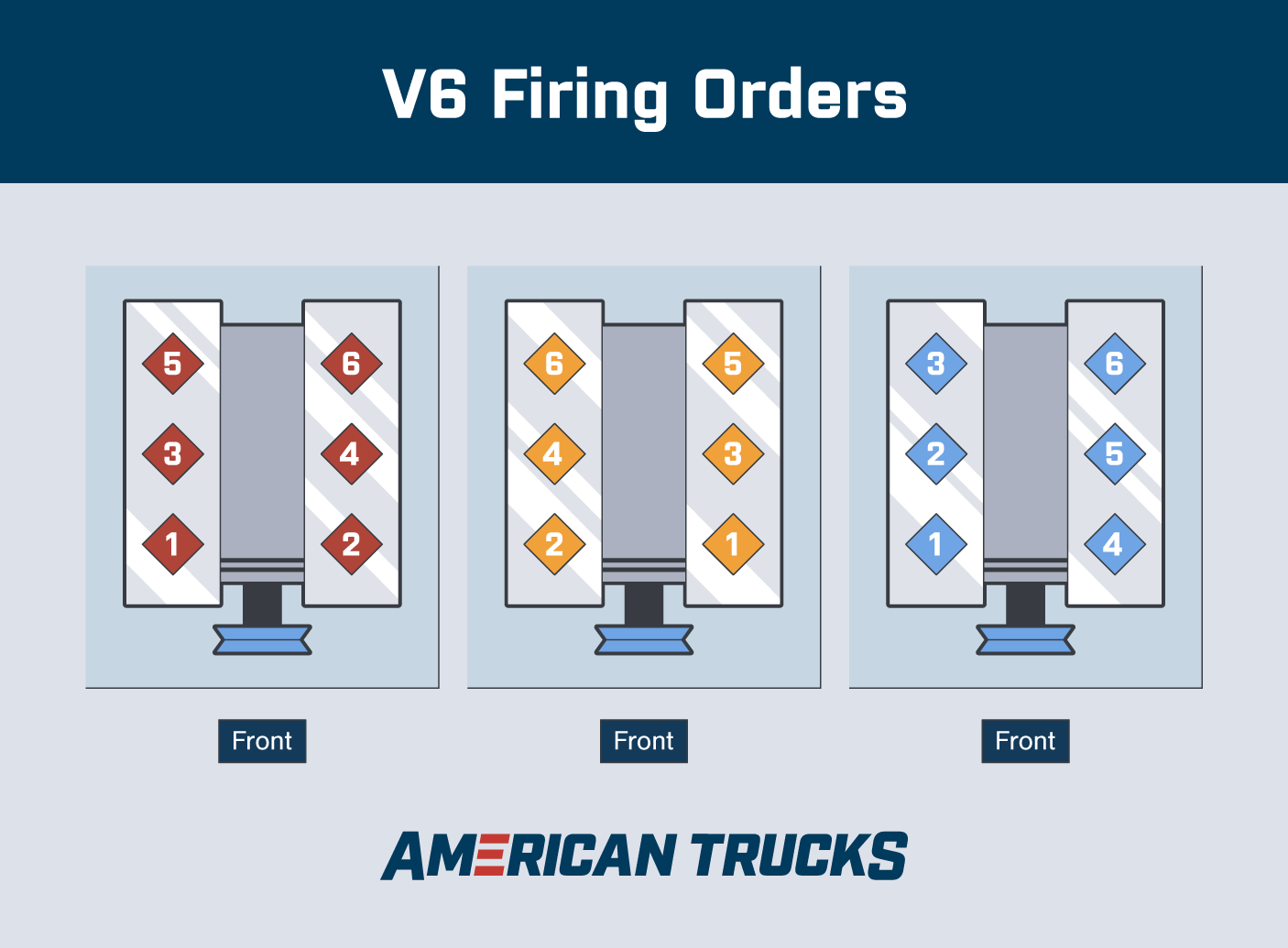
Typically, the firing order of a V6 engine alternates from left to right starting at the front (either on the left or the right, generally depending on which option is nearer to the crankshaft's front). For example, starting at the front of the vehicle, a GM V6's order would be 1-3-5 on the left and 2-4-5 on the right, a consecutive 1-6 zigzag.
On other V6 engines, the order may run front to back on one side and then front to back on the other. A Ford V6, for example, would be ordered 1-2-3 from front to back on the right side and 4-5-6 from front to back on the left side.
Size and Position
Comparable to a traditional inline-four, the layout of a V6 engine makes it more compact, so it tends to be a better option for a wider range of body sizes that might not otherwise fit a straight-six engine. It's like trying to fit a hamburger in a lunchbox instead of a 12" sub. V6 engine blocks are also positioned lower toward the ground, which in turn creates a lower center of gravity that improves handling.
Movement
Because the two rows of cylinders in V6 engines fire at opposing angles with long strokes, they create more side-to-side movement. There are balancing shafts with counterweights in the engine meant to reduce this movement, but they can't counteract 100% of the vibrations created by the firing cylinders.
Benefits of a V6 Engine
These details may sound great, but what do they mean in practice? The size and position of a V6 engine provide the following benefits:
- Compact: V6 engines have a smaller footprint, opening up more space for mods like turbochargers.
- Balanced: With its lower position, a V6 engine has a lower center of gravity and more even weight distribution.
- Versatile: The "V" configuration of a V6 engine allows manufacturers to drop a six-cylinder engine into a vehicle that otherwise would only have been able to accommodate a four-cylinder inline engine. Its shorter size also allows it to be used in a front-wheel-drive vehicle.
Drawbacks of a V6 Engine
V6 engines may be more widely driven than straight-sixes, but they do come with a few drawbacks.
- Maintenance Complexity: With double the amount of valvetrain components to accommodate the V6 structure's two cylinder banks, there are more parts of a V6 to repair and maintain.
- More Vibrations: The construction of a V6 engine is less balanced than a straight-six, leaving more room for movement from the cylinders and leading to increased vibrations throughout the crankshaft.
- Less Reliable: For those who rely on power performance, V6 engines aren't generally as prized for longevity as straight-six engines.
|
Pros:
|
Cons:
|
|
Compact
|
Maintenance complexity
|
|
Balance
|
More vibrations
|
|
Versatile
|
Less reliable
|
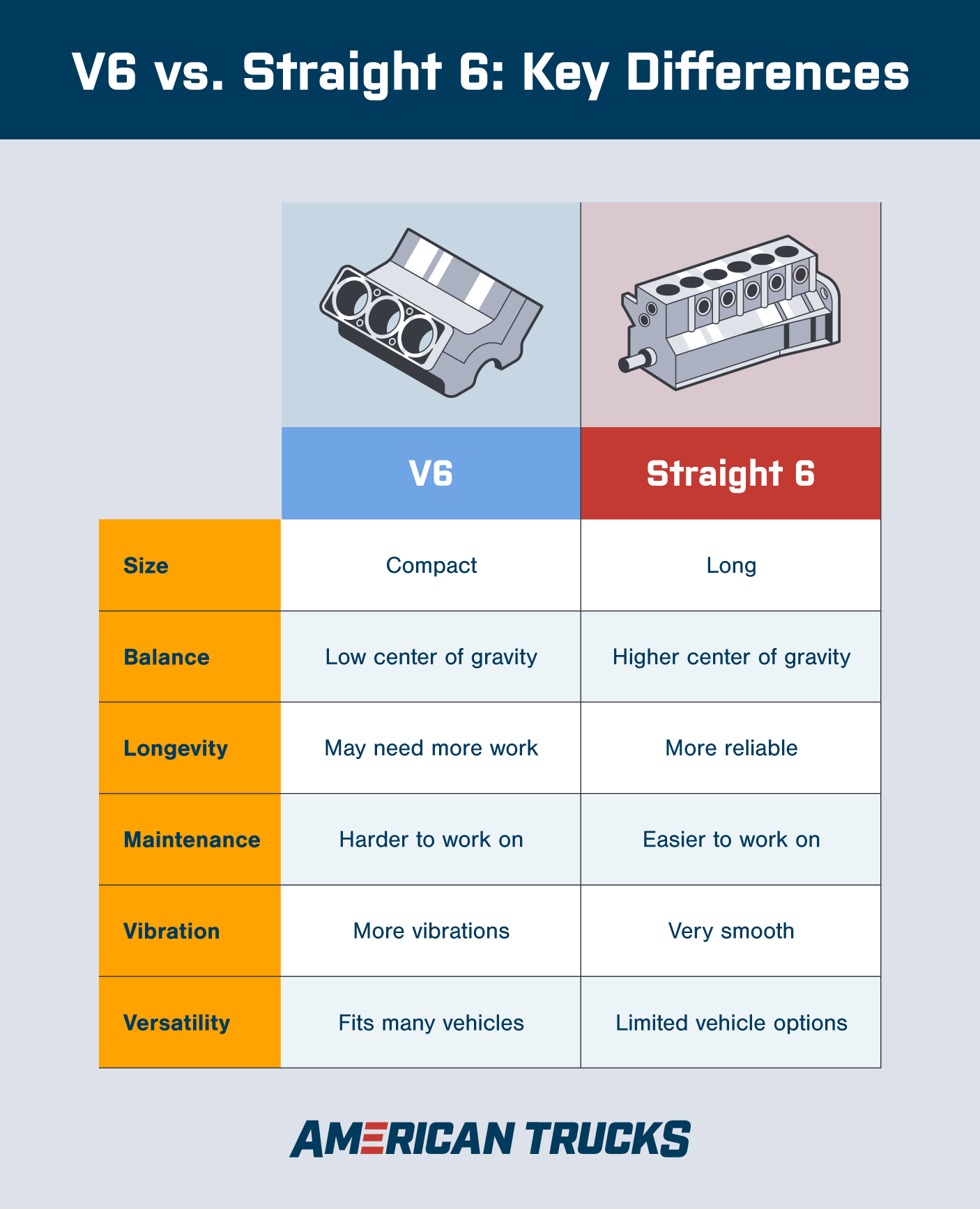
V6 vs. Straight 6: Key Differences
So you know that V6 engines are shaped like a V and straight-six engines form a straight line—but what's all that really mean for you, the driver? If you're looking for the real key differences between V6 and straight-six engines tied up in a neat package, here's the long and short of it.
V6 vs. Straight 6: Which Is Better?
If you're still undecided on the V6 vs. straight-six debate, consider that most die-hard performance fanatics seem to fall on the straight-six side—but that doesn't make it a clear winner.
- From a pure performance perspective, inline engines have the better blend of performance, reliability, and ease of repairing or replacing engine components.
- From a production standpoint, V6 engines tend to make more sense for adding six-cylinder power to vehicles with maximum interior space and front-wheel drive.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is a Straight 6 the Same as a V6?
Straight-six (or inline-six) and V6 engines both have six cylinders, but they are arranged very differently. Straight-six engines are long, tall, and narrow, with the cylinders aligned in a single row, typically running from front to back. V6 engines are more compact, with two rows of three cylinders angled in a V shape.
Is a Straight 6 More Powerful Than a V6?
Straight-six engines are known to be more performance-friendly than V6 engines, offering more reliable power and greater torque.
What Does V6 Mean?
V6 refers to the V-shaped arrangement of six cylinders on an engine, with the cylinders angled downward at typically 60 or 90 degrees. By contrast, in a straight-six or inline-six engine, the six cylinders are arranged vertically in a single straight line.
More Engine Guides:




